Is your hunger emotional or physical?
Learn to identify the difference.
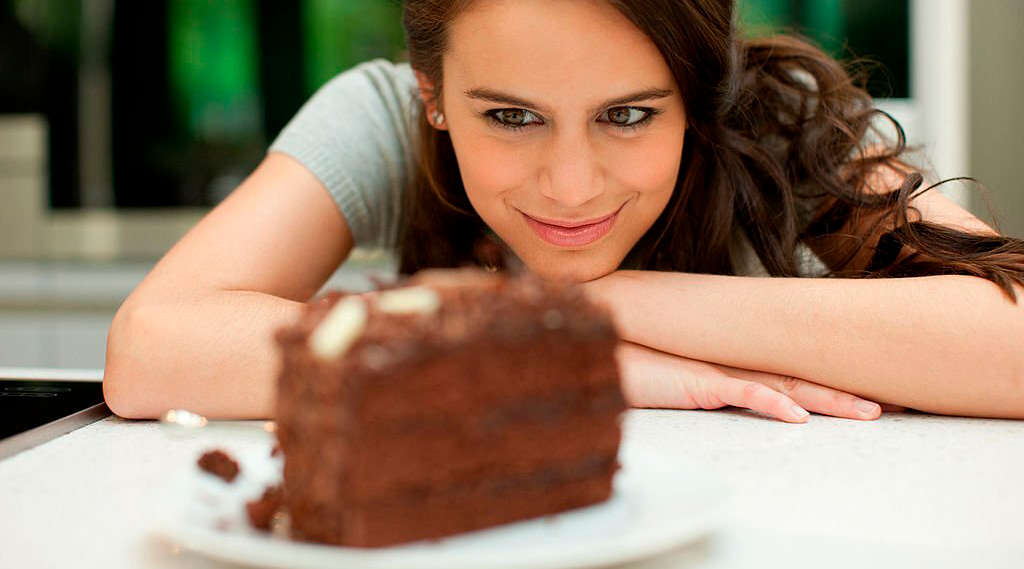

Emotional hunger
is still a topic that has been gaining prominence in discussions about mental
health, weight gain and illnesses. The act of eating is not just related to
satisfying hunger or nutrition, the emotional side is also present. All of our
foods choices end up influencing our actions and reactions in a positive or
negative way, our food choices provide different sensations, memories and
emotions. When eating in reaction to an emotion, this mechanism tends to be
automatic and the choices also tend to be based on taste, such as sweets and highly
palatable fats, which end up being consumed in large portions and it was from
this reflection that the term “emotional hunger” emerged.
Emotional hunger
is independent of the individual's energetic and nutritional needs, expressed
by the desire to eat according to the emotional state. It is usually linked to
negative emotions, stress or when we reward ourselves for small everyday
victories.
Physiological
hunger or real hunger arises when the body has to supply the energetic and
nutritional needs, essential to its proper functioning through food, it is not
linked to any specific food.
How to identify emotional hunger?
The main
indications that it is out of control are the urgent desire to eat, the
ingestion of food with voracity or in great quantity and difficulty to control
or the sensation that it satisfies nothing. In practice, it is like the
representation "live to eat" and not "eat to live". Know
how to differentiate and ask yourself if it is really physiological hunger.
Emotional hunger:
1. Suddenly
appears
2. The ingestion
of a type of food that represents a "comfort"
3. Urgent need,
it is not possible to wait for the meal
4. It does not
stop eating, even if satiated
5. It disappears
when some distraction arises with another activity
6. It causes
negative sensations after the meal, such as guilt and frustration
Physiological hunger
1. It appears
gradually
2. The ingestion
of a meal or snack is more complete and varied
3. As it
manifests gradually, it is usually possible to wait a while to eat
4. When
satiated, you no longer feel the need to eat
5. It does not
disappear when performing another task
6. It causes positive sensations after eating, such as pleasure and well-being
How to treat emotional hunger?
Food can serve
as a momentary relief, but it is not a treatment for emotional hunger. Those
who suffer from this compulsion and do not pursue solutions and treatments may
end up losing the ability to deal with their emotions and gaining weight and
compromising their health. In this case, an incorrect diet combined with a lack
of physical exercise can lead to several illnesses such as: hypertension, high
cholesterol, diabetes, sleep apneas, cardiovascular problems, depression and
anxiety. It is advisable to seek
professional help in these situations as a follow-up with a professional may be
all you need to break these habits and improve your health.
Most Popular:
-
Sciton HALO vs Sciton BBL
Read More »September 20, 2022 -
What is profhilo, and how is it different from fillers?
Read More »September 20, 2022 -

Body contour solutions from SKIN111
Read More »September 20, 2022 -

Does IV GLUTATHIONE therapy work
Read More »September 20, 2022 -

How can an IV drip help you boost your energy
Read More »September 20, 2022